About me
I am currently a tenure-track assistant professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) at the University of Arkansas, working on terahertz (THz) science and technology.
My career has been shaped by a global perspective. I pursued my master’s degree at Tsinghua University before venturing to the United States for my Ph.D. degree at Georgia Institute of Technology. During my Ph.D. studies, I had the incredible opportunity to go to Europe and conduct research in the joint international laboratory between Georgia Tech and CNRS, the French national laboratory system. After obtaining my Ph.D. degree, I joined the National Institute of Scientific Research (INRS) in Canada, where I served as the group leader and managed research activities related to THz photonics.
I am passionate about exploring the fundamental principles and practical applications of THz radiation, particularly in the areas of imaging, sensing, and communications. My work has been published in ~30 peer-reviewed journals, ~40 conference proceedings, and 5 patents. I am a member of IEEE, Optica, and SPIE.
- Terahertz (THz) Technology
- Imaging and Sensing
- Communications
- Biophotonics
- Nondestructive Evaluation
-
Ph.D. in Electrical and Computer Engineering
Georgia Institute of Technology, USA
-
M.Sc. in Control Science and Engineering
Tsinghua University, China
Recent News
Research Themes
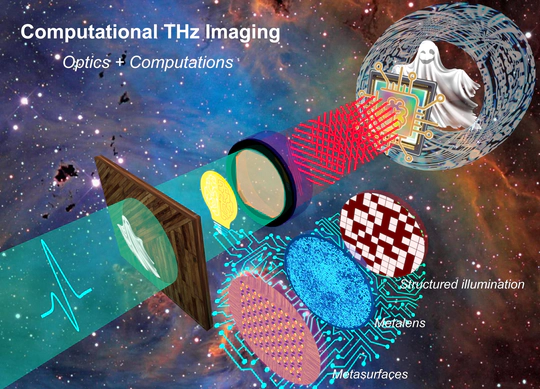
Our research spans the terahertz (THz) region of the electromagnetic spectrum, situated between the microwave and infrared light, bridging the gap between electronics and photonics. This fascinating frequency range is well worth exploring due to the unique properties of THz radiation and closing this technological gap promises to unlock a variety of groudbreaking solutions for transformative applications.
Featured Publications
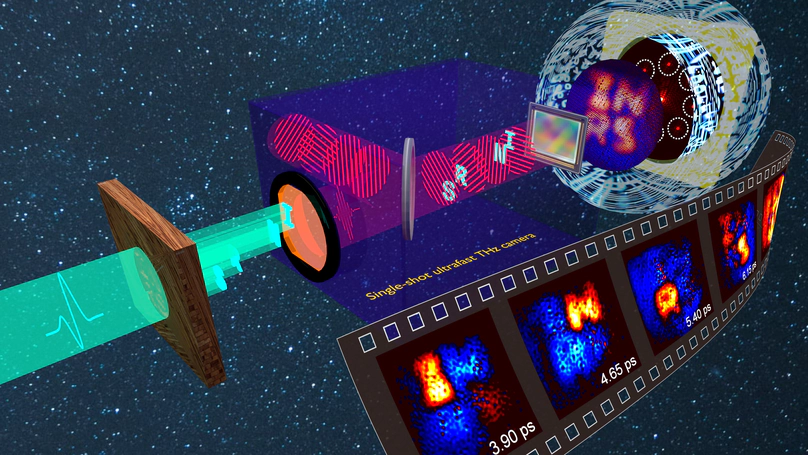
Multidimensional imaging of transient events has proven pivotal in unveiling many fundamental mechanisms in physics, chemistry, and biology. In particular, real-time imaging modalities with ultrahigh temporal resolutions are required for capturing ultrashort events on picosecond timescales. Despite recent approaches witnessing a dramatic boost in high-speed photography, current single-shot ultrafast imaging schemes operate only at conventional optical wavelengths, being suitable solely within an optically-transparent framework. Here, leveraging on the unique penetration capability of terahertz radiation, we demonstrate a single-shot ultrafast terahertz photography system that can capture multiple frames of a complex ultrafast scene in non-transparent media with sub-picosecond temporal resolution. By multiplexing an optical probe beam in both the time and spatial-frequency domains, we encode the terahertz-captured three-dimensional dynamics into distinct spatial-frequency regions of a superimposed optical image, which is then computationally decoded and reconstructed. Our approach opens up the investigation of non-repeatable or destructive events that occur in optically-opaque scenarios.
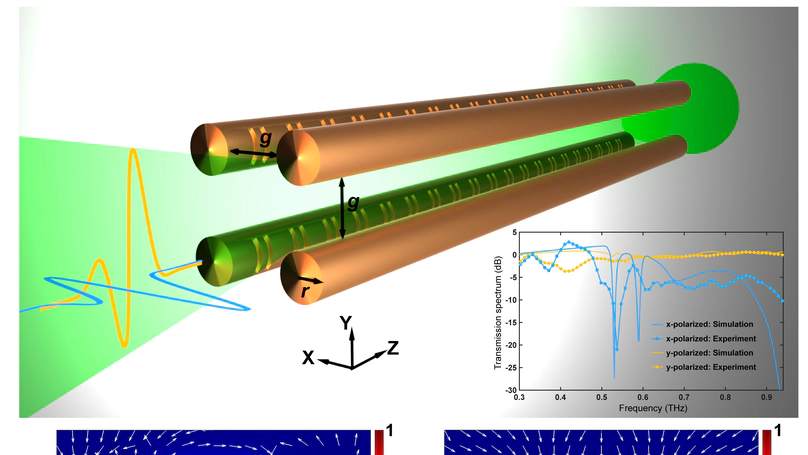
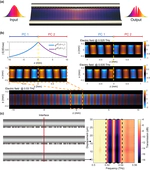
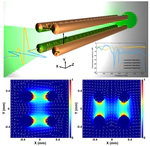
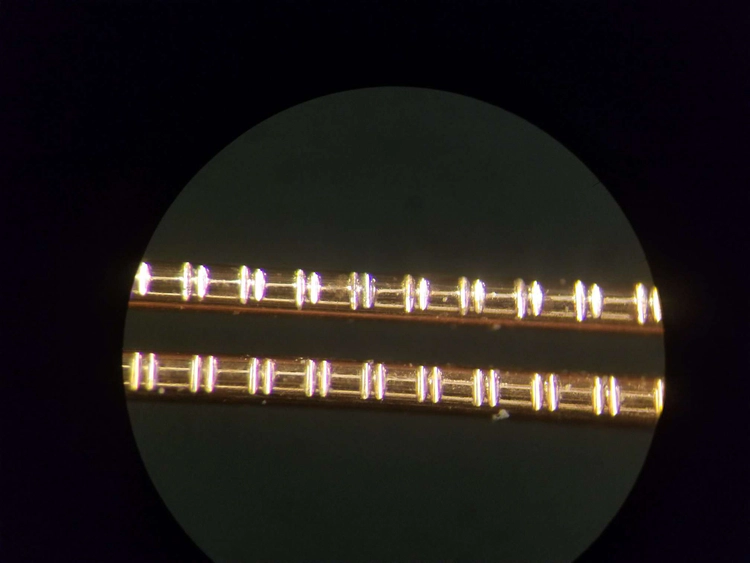
Waveguides play a pivotal role in the full deployment of terahertz communication systems. Besides signal transporting, innovative terahertz waveguides are required to provide versatile signal-processing functionalities. Despite fundamental components, such as Bragg gratings, have been recently realized, they typically rely on complex hybridization, in turn making it extremely challenging to go beyond the most elementary functions. Here, we propose a universal approach, in which multiscale-structured Bragg gratings can be directly etched on metal-wires. Such an approach, in combination with diverse waveguide designs, allows for the realization of a unique platform with remarkable structural simplicity, yet featuring unprecedented signal-processing capabilities. As an example, we introduce a four-wire waveguide geometry, amenable to support the low-loss and low-dispersion propagation of polarization-division multiplexed terahertz signals. Furthermore, by engraving on the wires judiciously designed Bragg gratings based on multiscale structures, it is possible to independently manipulate two polarization-division multiplexed terahertz signals. This platform opens up new exciting perspectives for exploiting the polarization degree of freedom and ultimately boosting the capacity and spectral efficiency of future terahertz networks.
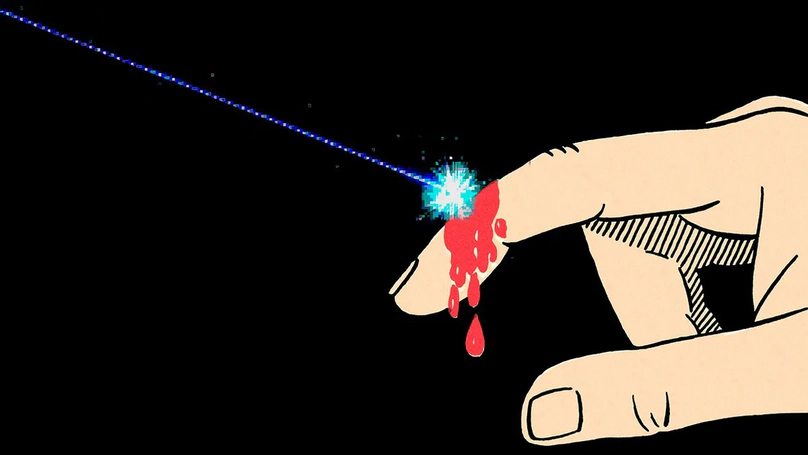
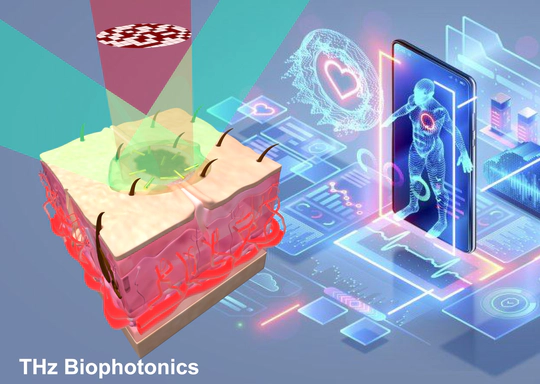
In view of minimally-invasive clinical interventions, laser tissue soldering assisted by plasmonic nanoparticles is emerging as an appealing concept in surgical medicine, holding the promise of surgeries without sutures. Rigorous monitoring of the plasmonically-heated solder and the underlying tissue is crucial for optimizing the soldering bonding strength and minimizing the photothermal damage. To this end, we propose a non-invasive, non-contact, and non-ionizing modality for monitoring nanoparticle-assisted laser-tissue interaction and visualizing the localized photothermal damage, by taking advantage of the unique sensitivity of terahertz radiation to the hydration level of biological tissue. We demonstrate that terahertz radiation can be employed as a versatile tool to reveal the thermally-affected evolution in tissue, and to quantitatively characterize the photothermal damage induced by nanoparticle-assisted laser tissue soldering in three dimensions. Our approach can be easily extended and applied across a broad range of clinical applications involving laser-tissue interaction, such as laser ablation and photothermal therapies.
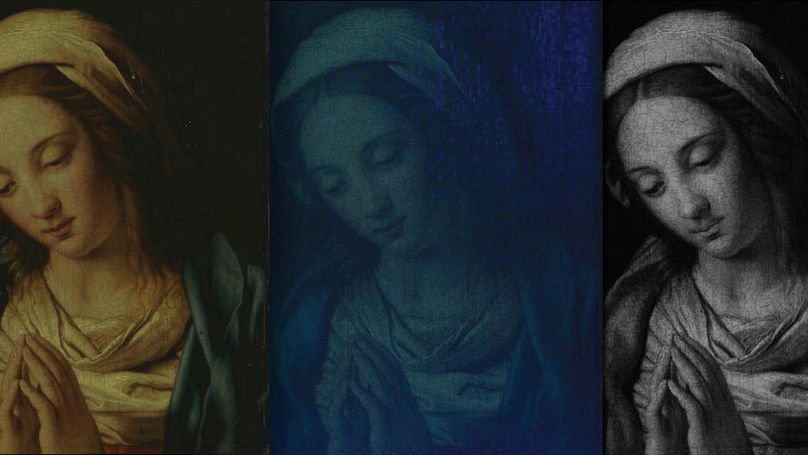

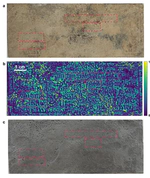
The process by which art paintings are produced typically involves the successive applications of preparatory and paint layers to a canvas or other support; however, there is an absence of nondestructive modalities to provide a global mapping of the stratigraphy, information that is crucial for evaluation of its authenticity and attribution, for insights into historical or artist-specific techniques, as well as for conservation. We demonstrate sparsity-based terahertz reflectometry can be applied to extract a detailed 3D mapping of the layer structure of the 17th century easel painting Madonna in Preghiera by the workshop of Giovanni Battista Salvi da Sassoferrato, in which the structure of the canvas support, the ground, imprimatura, underpainting, pictorial, and varnish layers are identified quantitatively. In addition, a hitherto unidentified restoration of the varnish has been found. Our approach unlocks the full promise of terahertz reflectometry to provide a global and detailed account of an easel painting’s stratigraphy by exploiting the sparse deconvolution, without which terahertz reflectometry in the past has only provided a meager tool for the characterization of paintings with paint-layer thicknesses smaller than 50 μm. The proposed modality can also be employed across a broad range of applications in nondestructive testing and biomedical imaging.
Recent Publications
Recent Talks
Contact
- jd158@uark.edu
- 1 University of Arkansas Fayetteville, Fayetteville, AR 72701
- Bell 3183
- Follow Me